VNG Testing: A Vital Tool in Evaluating Vertigo and Dizziness Disorders
Do you have problems tracking objects or difficulty reading?
Complete Guide to VNG Test for Traumatic Brain Injury Patients
VNG Testing: The Revolutionary Approach to Diagnosing and Treating Traumatic Brain Injuries
Traumatic brain injuries can have a lasting impact on a person’s overall health and well-being. One of the symptoms that can arise after a traumatic brain injury is balance issues, which can lead to a wide range of problems. One way that healthcare professionals diagnose and evaluate balance issues is through VNG (videonystagmography) testing. If you’ve never heard of VNG testing before, don’t worry – this post will provide you with all the information you need to understand what it is, how it works, and who might benefit from it.


Understanding the Importance of VNG Testing
After a Traumatic Brain Injury
Understanding Videonystagmography Testing
1
What Is Videonystagmography Testing?
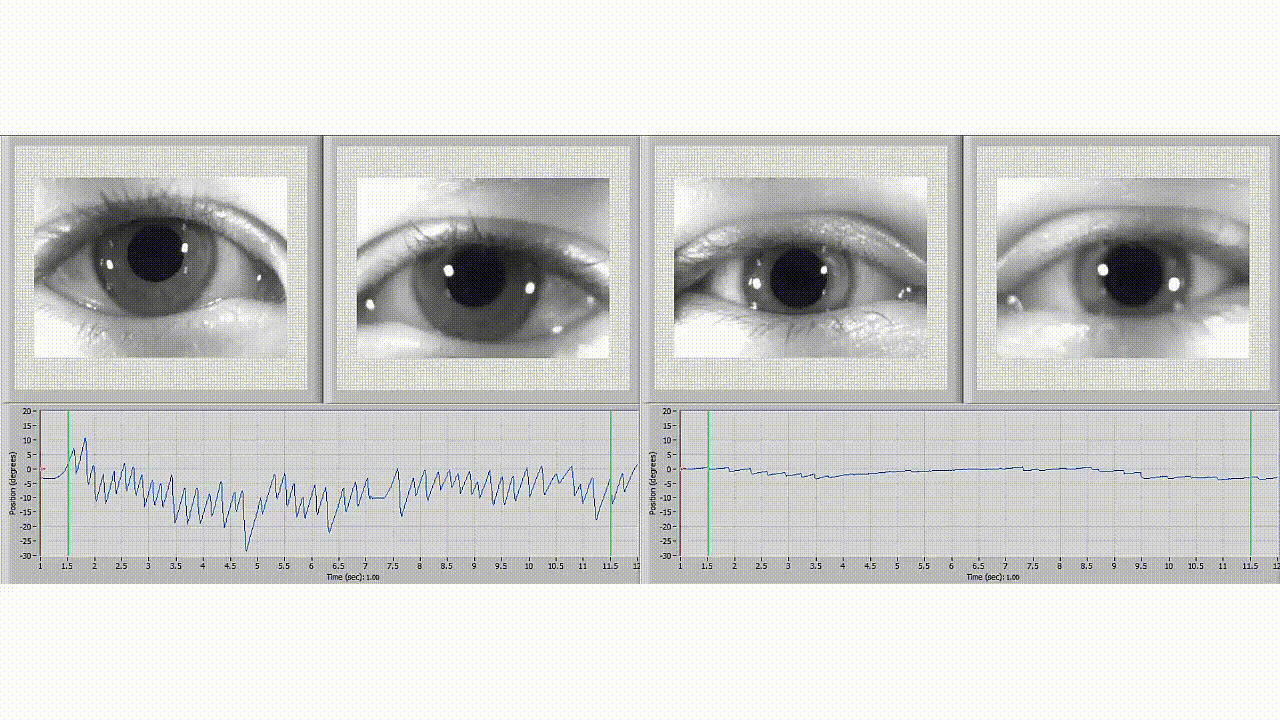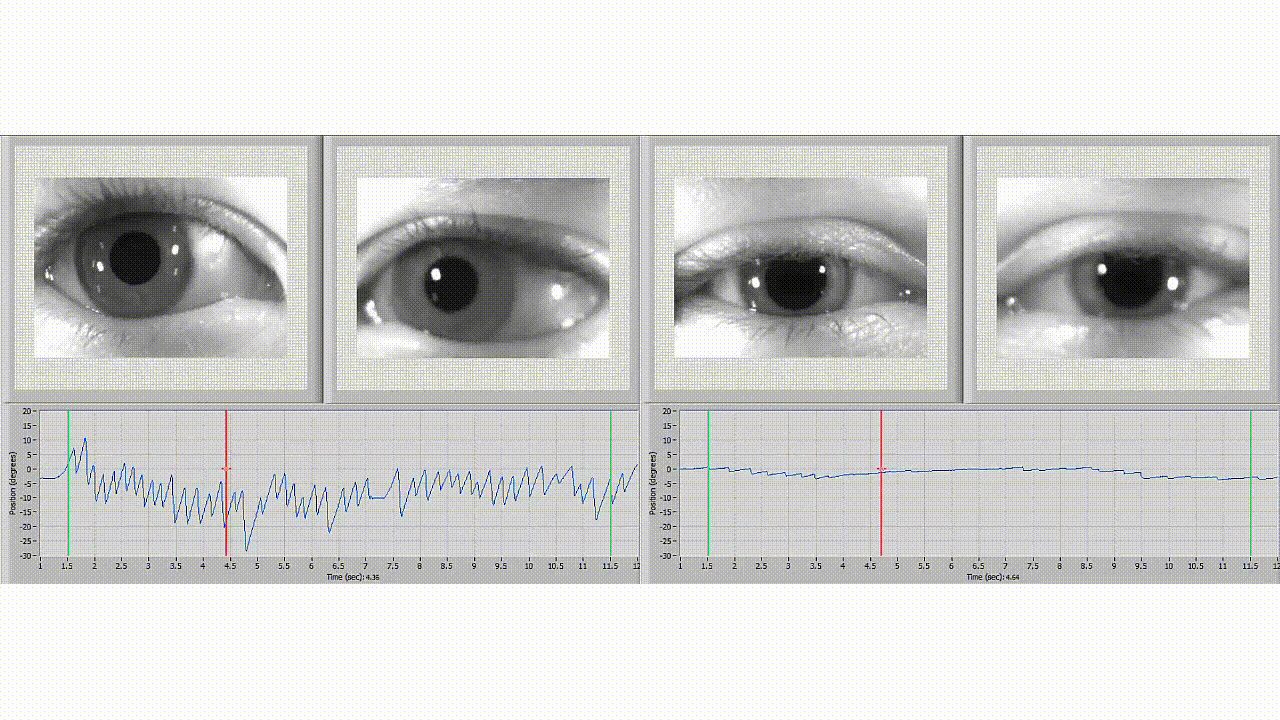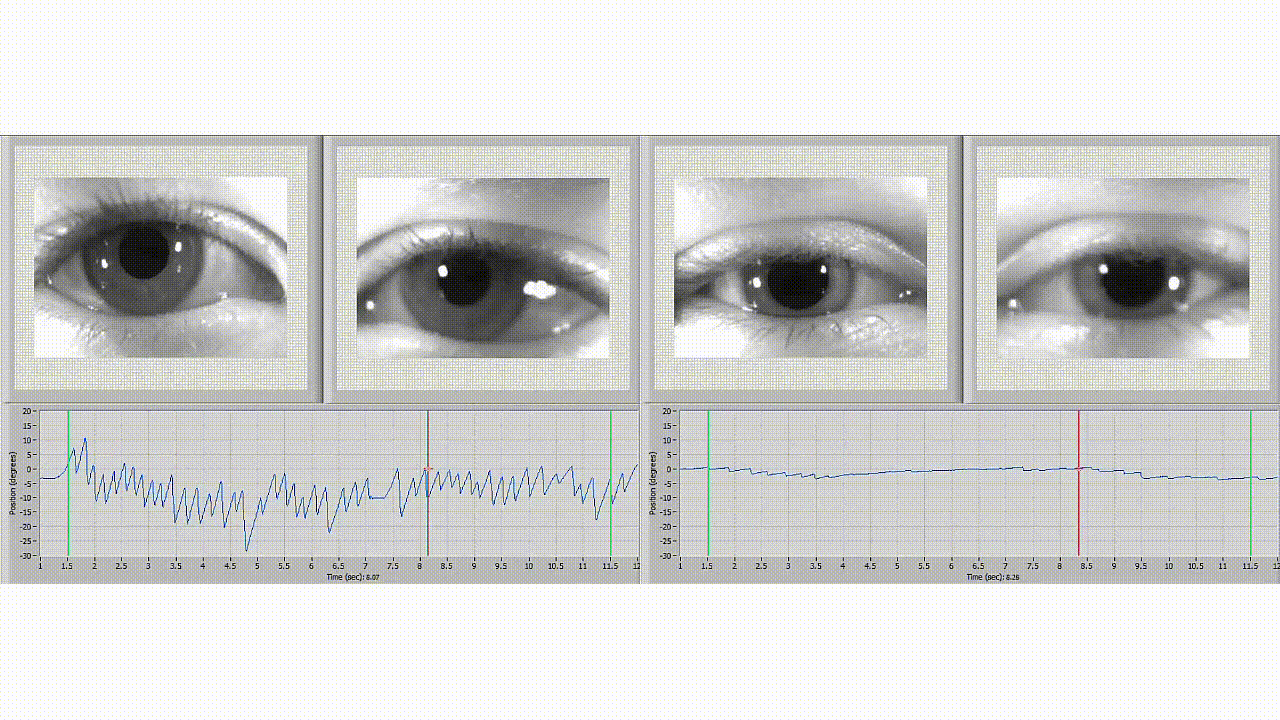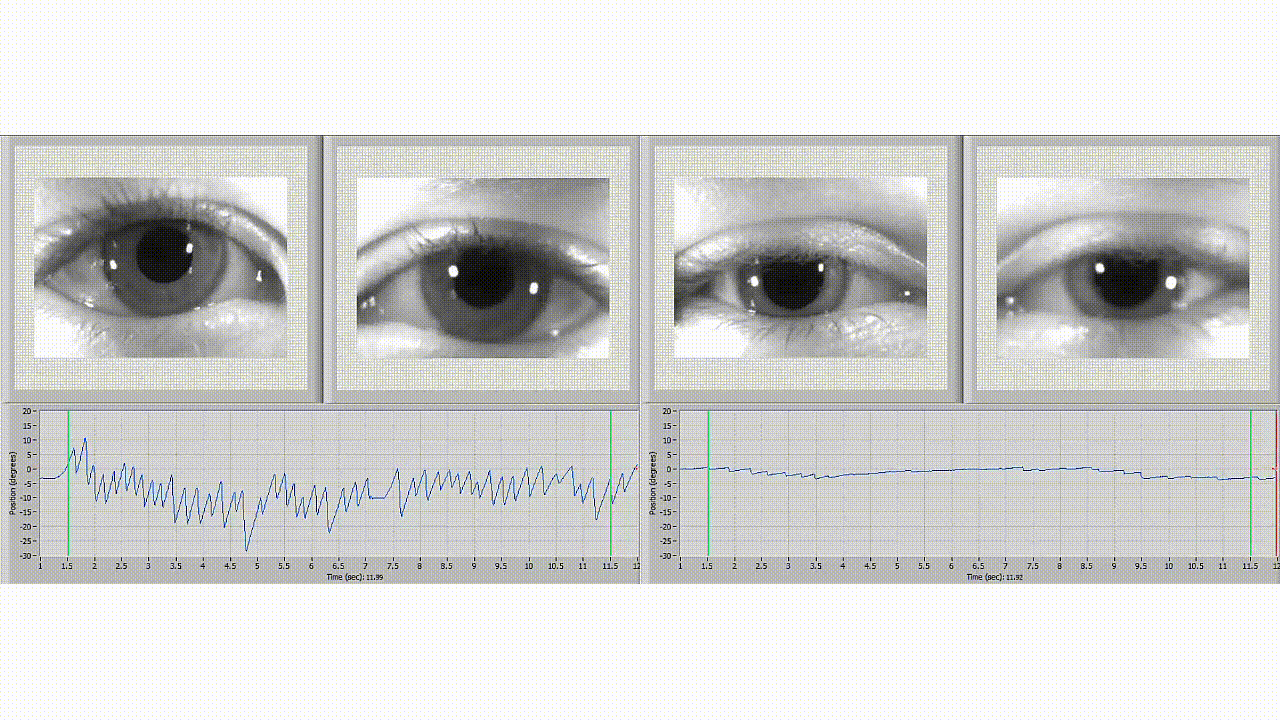
It is a diagnostic test that measures a patient's eye movements and evaluates the balance system's effectiveness. This test uses video technology to record and analyze a patient's eye movements while they complete a series of movements to test balance, such as moving their head in different directions or following a moving target with their eyes. This non-invasive and painless test makes it an ideal option for many patients.
2
How Does VNG Testing Work?
During a testing session, a healthcare professional will use infrared video cameras or goggles to track a patient's eye movements. A series of tests are performed that assess the function of the inner ear, eye movements, and nervous system. A patient wears goggles or infrared cameras to track eye movement. Different tests are used to evaluate different parts of the balance system, such as the vestibular system, which contributes to balance and stability.
3
What Are The Types Of VNG Testing?
There are different types of VNG tests that healthcare professionals may use to diagnose and evaluate balance issues. The most common types of tests include:
• Caloric testing – uses hot and cold air or water to stimulate the inner ear and measure the response.
• Dynamic positioning – involves the patient lying down, sitting up, or moving into different positions while their eye movements are tracked.
• Optokinetic testing – involves a moving target that the patient follows with their eyes to measure eye movements and visual tracking.
• Head impulse testing – involves quick, sudden head movements to measure the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR), which contributes to balance and stabilization of vision.
• Posturography – involves standing on a platform and tracking the pressure changes to determine balance.
4
What to Expect From a VNG Test Session?
Testing sessions typically last between 60-90 minutes. Patients are advised to wear comfortable clothing and avoid caffeine or other stimulants before the test. Patients will perform different movements during the test while wearing infrared cameras or goggles. It's important to follow the healthcare professional's instructions and remain still during the test to ensure accurate results.
5
Who Might Benefit From VNG Test?
Patients who experience balance issues or dizziness after a traumatic brain injury may benefit from VNG testing. This test can help healthcare professionals diagnose the cause of the balance issues and develop an effective treatment plan. VNG testing is also used to evaluate patients with vertigo, migraines, and other conditions that affect the balance system.
6
Risks of Videonystagmography Testing
The testing is generally considered safe and non-invasive, but there are some risks associated with the test. Some patients may experience dizziness or nausea during the test due to the movements involved. If this occurs, the test may need to be rescheduled. Patients should also inform their healthcare professional if they are pregnant, have a pacemaker, or have other medical conditions that may make VNG testing unsafe.
7
What Are The Side Effects Of VNG Test?
Most patients do not experience any side effects from the testing. In some cases, patients may feel dizzy or disoriented during or after the test. This is usually temporary and will resolve with time. It's important to inform your healthcare professional if you experience any unusual symptoms.
8
Who Shouldn't Use VNG Test?
Videonystagmography testing is not recommended for patients who are pregnant or have certain medical conditions that may make the test unsafe. Patients with pacemakers or other implanted devices should also avoid VNG testing, as it may interfere with the device's function. Your healthcare professional will evaluate your medical history and determine if VNG testing is safe for you.
9
What Are Other Testing Options for balance issues?
VNG testing is just one of several diagnostic tests that healthcare professionals may use to evaluate balance issues. Other tests include electrooculography (EOG), electronystagmography (ENG), and posturography. Your healthcare professional will evaluate your needs and recommend the most appropriate test.
Prepare for A VNG Testing
Steps to Prepare for VNG Testing
1. Medication Review
Certain medications can affect the results of VNG testing. You should inform your healthcare provider about all medications and supplements you are taking, including:
- Prescription medications
- Over-the-counter drugs
- Herbal supplements
Your healthcare provider may advise you to stop taking certain medications, such as:
- Antihistamines
- Sedatives
- Tranquilizers
- Sleeping pills
- Anti-dizziness medications
Typically, you’ll need to discontinue these medications 48 hours before the test, but always follow the specific instructions given by your healthcare provider.
2. Avoid Stimulants and Depressants
To ensure the most accurate test results, avoid the following substances for at least 24 hours before your VNG test:
- Caffeine (coffee, tea, soda, and chocolate)
- Alcohol
- Tobacco products
3. Dietary Restrictions
On the day of your test, it’s recommended to have a light meal. Avoid heavy or greasy foods that might upset your stomach. If you’re scheduled for morning testing, consider having a small, light breakfast.
4. Clothing and Accessories
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing to your appointment. Avoid wearing eye makeup, especially mascara or eyeliner, as these can interfere with the test equipment. If you wear contact lenses, consider wearing glasses instead on the day of the test.
5. Arrange Transportation
The VNG test can sometimes cause dizziness or imbalance temporarily. It’s wise to arrange for someone to drive you home after the test, as you may not feel comfortable driving yourself.
6. Rest Well
Ensure you get a good night’s sleep before the test. Being well-rested can help reduce anxiety and ensure you’re in the best possible condition for accurate testing.
What to Expect During the Test
Understanding the process can help reduce any anxiety you might have. Here’s a brief overview of what happens during VNG testing:
- Initial Evaluation: Your healthcare provider will review your medical history and symptoms.
- Eye Movement Tests: You’ll follow visual targets with your eyes while wearing special goggles.
- Positional Tests: Your head and body will be moved into various positions to observe how these changes affect your eye movements.
- Caloric Testing: Warm and cool air or water will be introduced into each ear canal to stimulate the inner ear, and your eye movements will be recorded.
The entire process is designed to be as comfortable as possible, and the healthcare team will guide you through each step.
Post-Test Care
After the test, it’s normal to feel a bit dizzy or unsteady. These sensations typically pass within a few minutes to a few hours. Make sure to rest and avoid any activities that require a high level of balance or coordination until you feel fully stable.
Interpreting VNG Results
Once the VNG tests are completed, the results can either be normal or abnormal.
Normal VNG Results
A normal VNG result indicates that the inner ear and the brain’s balance processing systems are functioning correctly. This means:
- No Significant Abnormalities: The patient’s eye movements are within the normal range, and there are no signs of vestibular dysfunction.
- Further Investigation Needed: If the patient continues to experience symptoms despite normal VNG results, other causes outside the vestibular system may need to be explored. This could include neurological conditions, cardiovascular issues, or psychological factors.
Abnormal VNG Results
An abnormal VNG result points to potential issues within the vestibular system. These results can help pinpoint the exact nature of the problem:
- Peripheral Vestibular Disorders: Conditions like benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), vestibular neuritis, or Ménière’s disease may be indicated by abnormal VNG results.
- Central Vestibular Disorders: Abnormalities might also suggest issues in the brainstem or cerebellum, such as multiple sclerosis or stroke.
- Customized Treatment Plan: Based on the specific findings, a targeted treatment plan will be developed. This could include vestibular rehabilitation therapy, medication, lifestyle modifications, or in some cases, surgical interventions.
Next Steps After VNG Testing
- Consultation with Healthcare Provider: Discuss the VNG results with your healthcare provider to understand the implications fully.
- Develop a Treatment Plan: If abnormalities are detected, your provider will create a treatment plan tailored to address the specific vestibular disorder.
- Follow-Up Tests: Additional testing or referrals to specialists (e.g., neurologists, otolaryngologists) may be necessary for comprehensive care.
- Lifestyle and Home Adjustments: Depending on the diagnosis, making changes at home and in daily activities to manage symptoms and improve quality of life may be recommended.
VNG testing is a valuable diagnostic tool for identifying the underlying causes of dizziness and balance disorders. Whether the results are normal or abnormal, understanding what they mean and the subsequent steps can significantly impact the management and treatment of these conditions. Always consult with your healthcare provider to ensure you receive the most appropriate care based on your VNG results.
You may benefit from a diagnostic test called videonystagmography (VNG). VNG is a non-invasive assessment healthcare professionals use to identify the root cause of balance disorders and determine the most effective treatment.
Maximizing your Recovery from Traumatic Brain Injuries with VideoNystagmoGraphy Testing
Get Back on Track with Accurate Diagnosis using VNG Testing: VNG testing can be important in diagnosing and evaluating balance issues after a traumatic brain injury.
This test is non-invasive, safe, and effective at evaluating the inner ear, eye movements, and nervous system. If you’re experiencing balance issues after a traumatic brain injury, talk to us about VNG testing and other diagnostic options. Early diagnosis and treatment can be critical for a successful recovery.
Blogs
In the world of neuroscience, one of the advanced tools used to understand brain function is the Quantitative Electroencephalogram (QEEG), often referred to as brain mapping. But who interprets these intricate brain maps, and why

Meet Our No.1 Best Neuropsychologist in Tampa, FL Location
At Radius TBI, we pride ourselves on providing exceptional care for individuals suffering from traumatic brain injuries (TBI) and concussions. Our integrated medical team in Tampa, FL, includes some of the most respected and experienced

Did you know? Dealing with a traumatic brain injury (TBI) often means navigating a range of complications, one of the most prevalent being sleep disturbances. Surprisingly, 30-70% of individuals with a TBI experience some form
Understanding Routine EEG, QEEG, and Ambulatory EEG Tests
EEG, QEEG, and Ambulatory EEG are distinct forms of electroencephalography, each serving unique purposes in the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological conditions.
A Deep Dive into Electromyography (EMG Test): Decoding the Language of Muscles and Nerves
Electromyography (EMG) is a diagnostic procedure that plays a crucial role in unraveling the intricacies of the neuromuscular system. By measuring the electrical activity within muscles and the nerves controlling them, EMG provides valuable insights