Revolutionize Your Brain Health:
The Power of EEG/Qeeg Brain Mapping
Integrative Care for Concussion / Traumatic Brain Injury Sufferers
in Ft. Lauderdale, Tampa, and Orlando, Florida
What is EEG Brain Mapping?
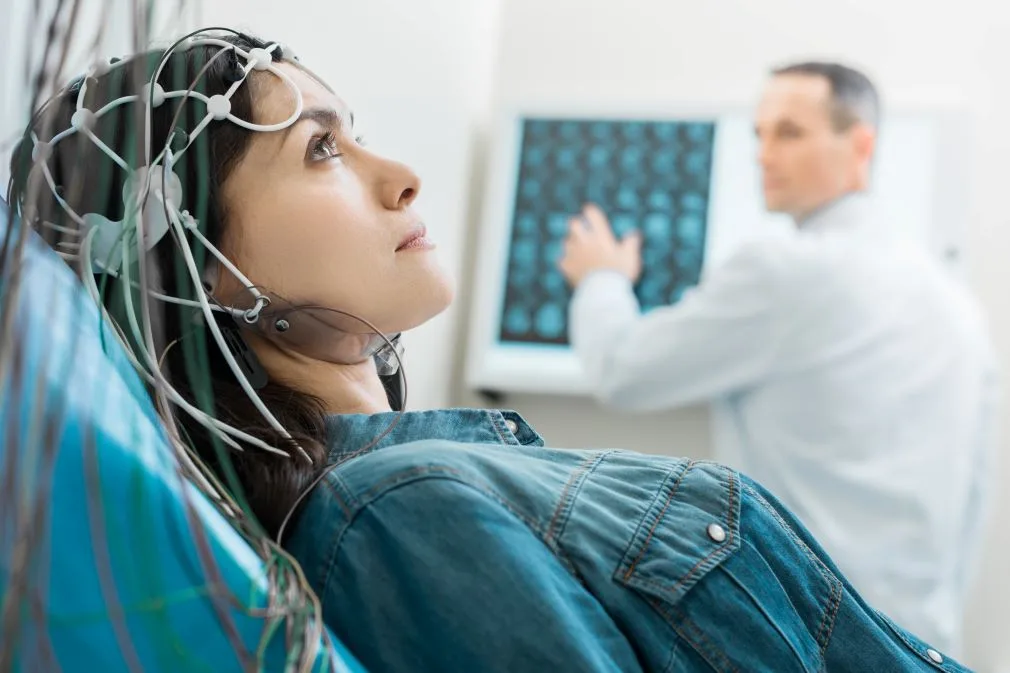
EEG stands for electroencephalogram. It is a test that measures and records the electrical activity of the brain. This is done by attaching small electrodes to the scalp, which detect and amplify the electrical signals generated by brain cells, or neurons. The resulting recording is called an EEG.
EEG is a non-invasive and painless procedure that is commonly used in medical settings to diagnose and monitor various neurological conditions. It helps healthcare professionals assess brain function and identify abnormalities in electrical activity. EEG is often used in the diagnosis and management of conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, head injuries, and certain psychiatric disorders.
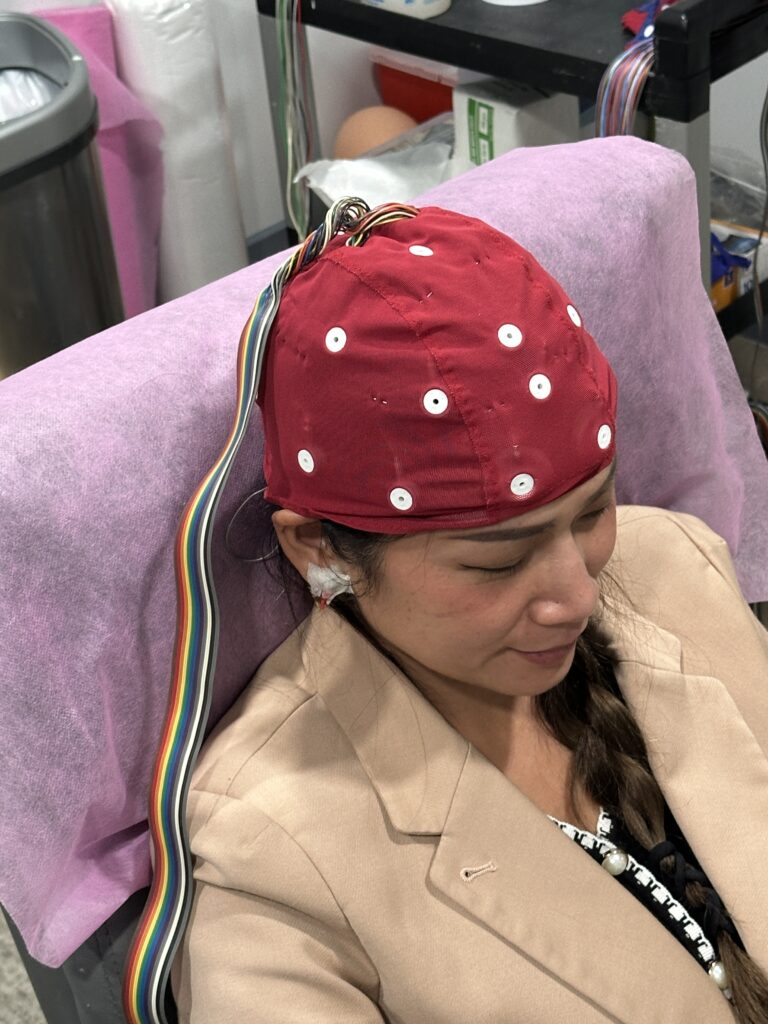
During an EEG, the patient typically sits or lies down, and the electrodes are attached to specific locations on the scalp using a conductive gel or paste. The electrical activity is then recorded and displayed as a series of wave patterns on a computer or paper. Different patterns and abnormalities in the EEG can provide valuable information about the brain’s functioning and help guide treatment decisions.
QEEG is a valuable tool for measuring and analyzing brain activity. Its objective and non-invasive nature make it a useful tool for diagnosing and monitoring a wide range of conditions. Its ability to provide information about the brain’s functional organization can be used to develop targeted interventions tailored to each patient’s individual needs. As technology advances, QEEG is likely to become an increasingly important tool in neuroscience, psychology, and medicine.
What is QEEG Brain Mapping?
QEEG, or quantitative electroencephalography, is a type of brain mapping that measures and analyzes brainwave activity using electrodes placed on the scalp.
Unlike traditional EEG, which only records brainwave patterns, QEEG converts the recorded data into color maps, known as brain maps. These maps visually represent brain activity, highlighting areas of the brain that are overactive, underactive, or functioning abnormally.
A powerful tool that allows researchers and clinicians to objectively measure and analyze brain activity. QEEG has numerous applications in neuroscience, psychology, and medicine and has been used to study a wide range of conditions, including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, anxiety, and traumatic brain injury.
What is Ambulatory EEG?
Ambulatory EEG, also known as ambulatory electroencephalography, refers to a type of EEG monitoring that allows for continuous recording of brain electrical activity over an extended period while the patient goes about their normal activities. Unlike a traditional EEG, which is typically performed in a medical facility and lasts for a short duration (usually around 20 to 60 minutes), ambulatory EEG monitoring can span a more extended period, such as 24 hours or several days.
The setup for ambulatory EEG involves the use of portable EEG equipment that is designed to be worn by the patient. This may include a small device with attached electrodes that can be secured to the patient’s scalp. The electrodes are connected to the portable recorder, which continuously records the electrical signals produced by the brain.
Ambulatory EEG is often used in cases where the intermittent nature of symptoms or events is a concern. For example, it can be valuable in the diagnosis and monitoring of certain types of epilepsy, where seizures may not occur during a brief in-office EEG but can happen unpredictably in daily life. By capturing a more extended period of brain activity, healthcare providers may have a better chance of detecting abnormal patterns and making a more accurate diagnosis.
This type of EEG monitoring allows patients to maintain their normal routines and activities, providing a more realistic picture of their brain function. After the monitoring period is complete, the recorded data is analyzed by healthcare professionals to identify any abnormal patterns or events that may be relevant to the patient’s condition.
How Does QEEG Work?
During the QEEG testing process, the patient sits comfortably while a clinician fits them with a cap that contains electrodes. These electrodes are painless and do not require any needles or injections. Once the electrodes are in place, patients are asked to perform tasks or exercises, such as tapping their fingers or solving puzzles.
The EEG machine records the brain’s electrical activity during these tasks, which is then analyzed using specialized software. The resulting data is converted into color maps, known as brain maps, which visually represent brain activity, highlighting areas of the brain that are overactive, underactive, or functioning abnormally.
It can also reveal areas of the brain that are not functioning optimally, enabling clinicians to create personalized treatment plans tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
Beyond the Surface: Unraveling Brain Patterns with EEG and QEEG Brain Mapping
Have you ever experienced brain fog, difficulty concentrating, or other cognitive issues? If so, you may benefit from a QEEG test. A non-invasive way of measuring brain activity. Contact us now!
Brain mapping testing, which may include techniques such as QEEG (quantitative electroencephalogram), traditional EEG, and ambulatory EEG, can be beneficial for various individuals and conditions. Here are some situations in which brain mapping testing might be useful:
QEEG testing can benefit anyone experiencing cognitive issues, including brain fog, difficulty concentrating, or memory problems. It can also be helpful for people diagnosed with ADHD, depression, or anxiety, as it can help identify specific areas of the brain that may be affected.
Unlike other methods of measuring brain activity, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) or positron emission tomography (PET), QEEG does not involve exposure to ionizing radiation or using contrast agents. This makes it a safe and convenient option for patients sensitive to these procedures. QEEG is also a non-invasive and relatively low-risk procedure.
Furthermore, QEEG testing can benefit many individuals who want to improve their cognitive performance, such as professionals or athletes. It can help them identify areas of the brain that may be underactive and develop targeted training programs to improve their performance.
Epilepsy Diagnosis and Monitoring: EEG and QEEG can be instrumental in diagnosing and monitoring epilepsy by detecting abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Ambulatory EEG is especially helpful in capturing intermittent seizures that may not occur during a short in-office EEG.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): In cases of traumatic brain injury, EEG and qEEG can help assess and monitor the impact of the injury on brain function. It may be used to identify areas of the brain affected by the injury and guide rehabilitation efforts.
Neurological Disorders: Brain mapping can be employed in the diagnosis and management of various neurological disorders, including but not limited to migraines, sleep disorders, and movement disorders.
Psychiatric Conditions: In some cases, brain mapping techniques are used to assess and understand brain function in individuals with psychiatric conditions, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or mood disorders.
Research and Cognitive Performance: Brain mapping is also utilized in research settings to study cognitive processes and brain function. It may be employed to investigate brain activity during tasks related to memory, attention, and decision-making.
Neurofeedback Training: QEEG can be used in neurofeedback therapy, a type of biofeedback that aims to regulate brain activity. It’s often used in conditions like ADHD, anxiety, and other behavioral disorders.
Stroke and Vascular Disorders: EEG and QEEG can provide information about brain function in individuals who have experienced strokes or vascular disorders.
Pre-surgical Planning: For certain medical conditions, such as epilepsy, where surgery may be considered as a treatment option, brain mapping can assist in identifying critical areas of the brain to avoid during surgery.
It’s important to note that the appropriateness of brain mapping testing depends on the specific clinical situation and the judgment of healthcare professionals. A neurologist or other qualified healthcare provider typically interprets the results and uses them in conjunction with other clinical information to make informed decisions about diagnosis and treatment.
If you or someone you know may benefit from QEEG brain mapping, we encourage you to schedule a consultation with our experienced healthcare professionals at Radius TBI.
Blogs
Recent Blogs

Meet Our No.1 Best Neuropsychologist in Tampa, FL Location
At Radius TBI, we pride ourselves on providing exceptional care for individuals suffering from traumatic brain injuries (TBI) and concussions. Our integrated medical team in Tampa, FL, includes some of the most respected and experienced professionals in the field, ensuring
Understanding Routine EEG, QEEG, and Ambulatory EEG Tests
EEG, QEEG, and Ambulatory EEG are distinct forms of electroencephalography, each serving unique purposes in the diagnosis and monitoring of neurological conditions.